Overview of China-Africa Trade Performance
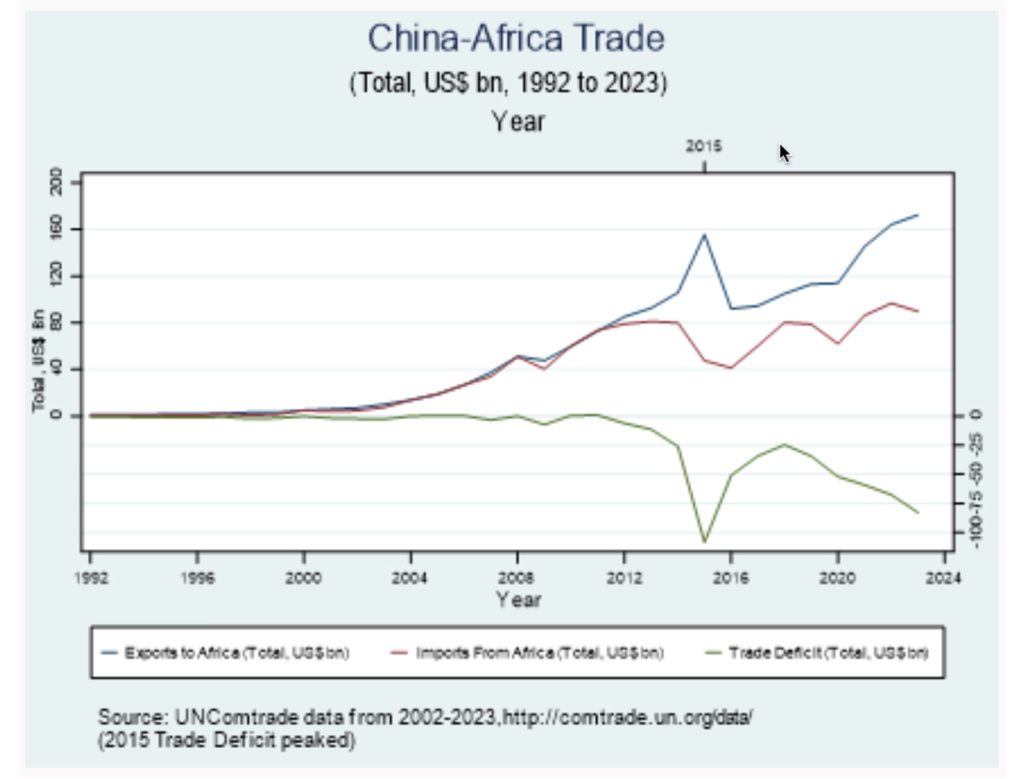
Official statistics from China’s General Administration of Customs show that trade between China and African countries reached a record high in the first five months of 2025. The trade volume increased by 12.4 percent year-on-year from January to May, to reach approximately $134 billion. This figure represents about 5.4 percent of China’s total foreign trade during the period under review. In 2023, China’s exports to Africa amounted to $173 billion, while imports from the Africa were valued at $110 billion, resulting in a trade deficit of $63 billion – more than half the value of its imports from Africa.
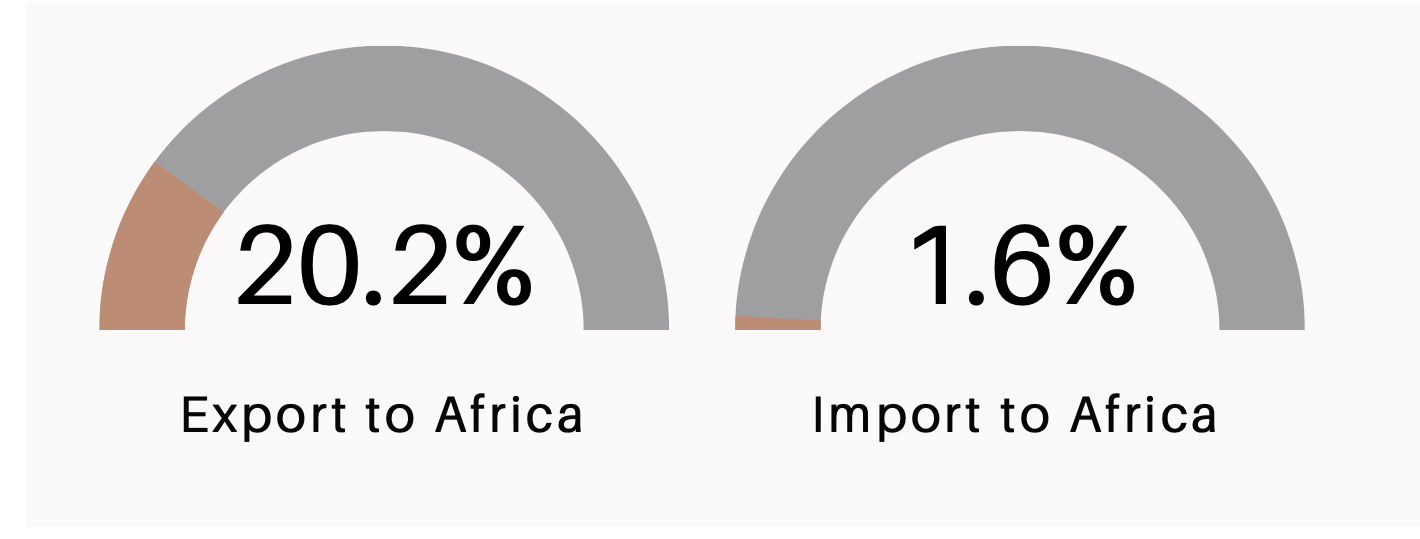
China’s exports to Africa surged by 20.2% in the first five months of 2025, reaching 599.57 billion yuan (approximately $83.51 billion). During the same period, China’s imports from Africa rose by 1.6%, totalling 363.64 billion yuan ($50.65 billion). During a press briefing in Accra, Ghana, on June 19 2025, Tong Defa, the Chinese ambassador to Ghana, highlighted these trade figures, noting that the record high for the five- month period underscores China’s position as Africa’s top trading partner for the past sixteen consecutive years. In his words, “the surge in trade is a testament to China’s commitment to deepening mutual prosperity with Africa and reflects not only the economic trust between the two regions but also reflects the growing maturity of China-Africa co-operation”.
Despite the growing trade volumes between China and Africa, global trade shocks particularly falling commodity prices, continue to impact Africa’s export revenues. For instance, while Chinese exports to Africa rose by 7.5% to reach $173 billion, imports from Africa declined by 6.7% to $109 billion. This imbalance widened Africa’s trade deficit with China to $64 billion in 2023, up from $46.9 billion in 2022, according to China’s Ministry of Commerce. Additionally, data from the UNCTAD database indicates that Africa’s trade deficit with China reached $32.86 billion in 2023, highlighting ongoing challenges in balancing trade between the two regions.
China – Africa Trade Performance
- Trade between China and Africa increased by 6.1% from 2023 to reach a record high of US $295 billion in 2024.
- Between January 1 and May 31 2025, trade between China and Africa had increased by 12.4% to reach approximately US$ 134 billion.
- Chinese exports to Africa rose by 3.5% to reach $178.76 billion in 2024
- Imports from Africa to China reached $116.79 billion, a 6.9% increase from 2023.
- Trade deficit continues to widen as trade volumes expand reaching $61.93 billion in 2024 (down from $64 billion).
Growth Rate from Jan-May 2025
China’s Strategic Initiatives to Strengthen Trade with Africa
To enhance trade and reduce the imbalance between China and Africa, China has taken strategic steps in recent years. At the 2024 Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC) Summit in Beijing, China announced its intention to remove all tariffs on exports from all 53 African countries with which it has diplomatic relations under the proposed Agreement on Joint Development Economic Partnership. This expands on a previous policy that granted zero-tariff treatment to 33 African least developed countries starting December 2024.
The Chinese government has also been deeply involved with the AfCFTA. To support Africa to advance integrated cooperation, China has agreed to actively participate in the development of the AfCFTA, and provide continued support to the AfCFTA secretariat. Some of these efforts include providing capacity-building support for the secretariat, and major infrastructure investments across Africa within the framework of the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC) Dakar Action Plan (2022-2024). Again in 2021, the AfCFTA secretariat and China’s Ministry of Commerce signed a memorandum of understanding to establish an expert group to collaborate and share experiences on intellectual property rights, customs procedures, digital trade, and competition policy, and to exchange concepts and progress on institutional capacity building for the implementation of AfCFTA.
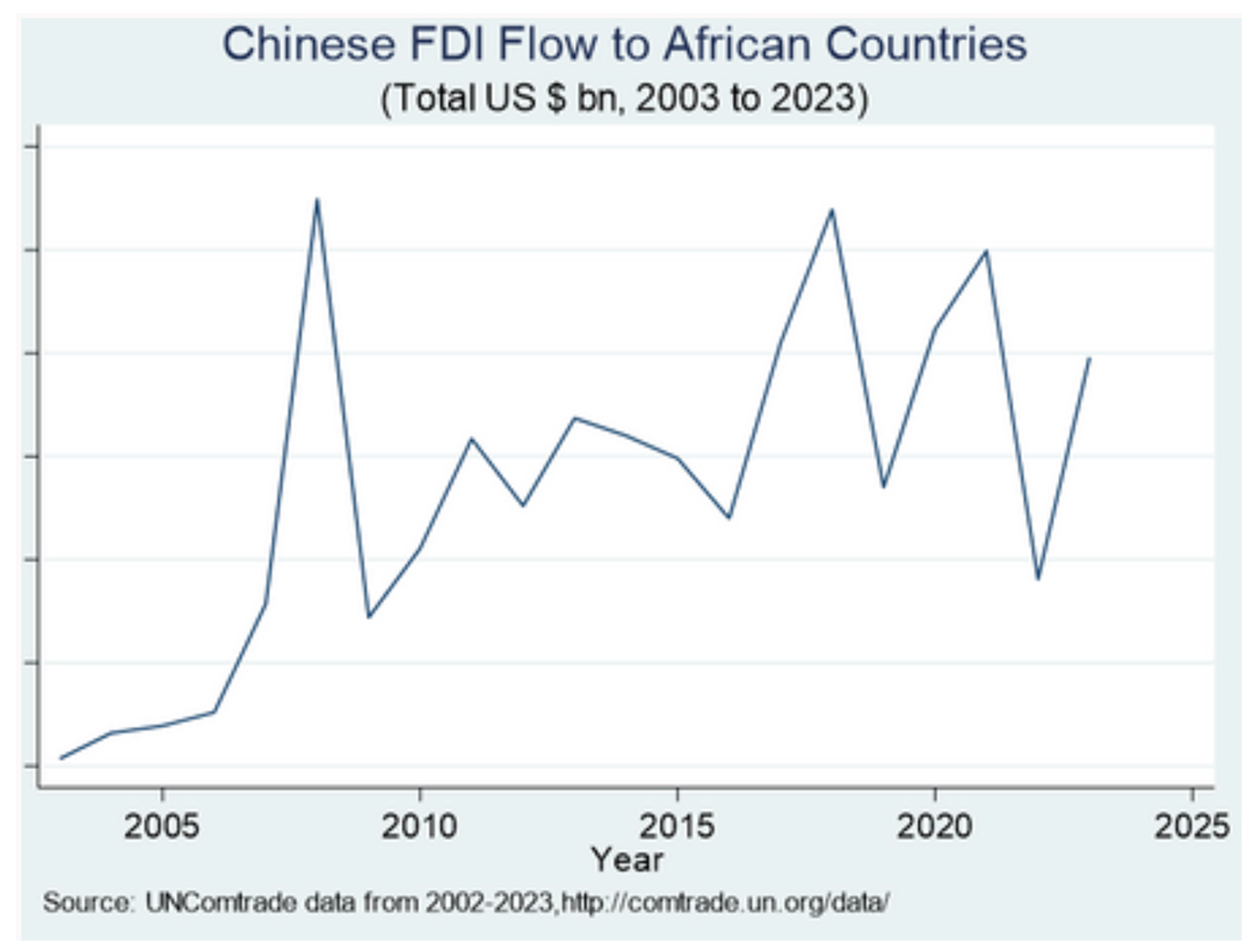
To add, since the ninth FOCAC summit in September 2024, China has provided approximately US $ 1.85 billion in new investments and about US $ 21 billion in development financing to Africa. These efforts have deepened China-Africa trade relations, with Chi a remaining Africa’s leading trading partner despite the widening trade imbalances.
What Products Does China Trade with Africa, and Who Are Its Key Partners?
China’s Major Exports to Africa
China mainly exports finished goods to Africa, such as textiles, machinery, and electronics
China’s Major Imports from Africa
African exports to China are dominated by raw materials like crude oil and gas, copper, cobalt, and iron ore
China’s Major Trading Partners in Africa in 2024
1.South Africa ( US $52.4 bn)
2.Democratic Republic of Congo (US $ 25.9 bn)
3.Nigeria ( US $21.8 bn)
4.Angola ( US20.8 bn)
Conclusion
Undoubtedly, China-Africa trade continues to deepen, with China firmly established as Africa’s leading trading partner despite persistent trade imbalances. To fully benefit from evolving trade agreements with China and to achieve the objectives of the AfCFTA, African nations should focus on transforming raw material exports into higher-value processed and manufactured products.
